When Waseem Alim, a Wharton graduate, decided to move back home in 2013 and launch an ecommerce company, there was zero buzz around startups on the streets of Bangladesh. Alim hoped to change that. “I realized I had skills that could be used to start a technology-based company in my home country,” he recalled.
From studying online retailers in other countries, Alim realized discounts were a major driver in convincing people to shop online. That, however, would mean high cash burn, not something an internet company in Bangladesh could afford.
So Alim decided to instead start an e-grocery company, which he named Chaldal. “Grocery demands loyalty because of its nature of repeat purchases,” said Alim. Given capital Dhaka’s notorious traffic, a grocery-delivery business made immense sense.
Since then, Chaldal has been a part of the prestigious startup incubator Y Combinator and received an investment from early-stage venture fund 500 Startups. The company’s current annual gross sales, or gross merchandise value, are estimated at $5 million, growing at over 100% every year.
From studying online retailers in other countries, Alim realized discounts were a major driver in convincing people to shop online. That, however, would mean high cash burn, not something an internet company in Bangladesh could afford.
So Alim decided to instead start an e-grocery company, which he named Chaldal. “Grocery demands loyalty because of its nature of repeat purchases,” said Alim. Given capital Dhaka’s notorious traffic, a grocery-delivery business made immense sense.
Since then, Chaldal has been a part of the prestigious startup incubator Y Combinator and received an investment from early-stage venture fund 500 Startups. The company’s current annual gross sales, or gross merchandise value, are estimated at $5 million, growing at over 100% every year.
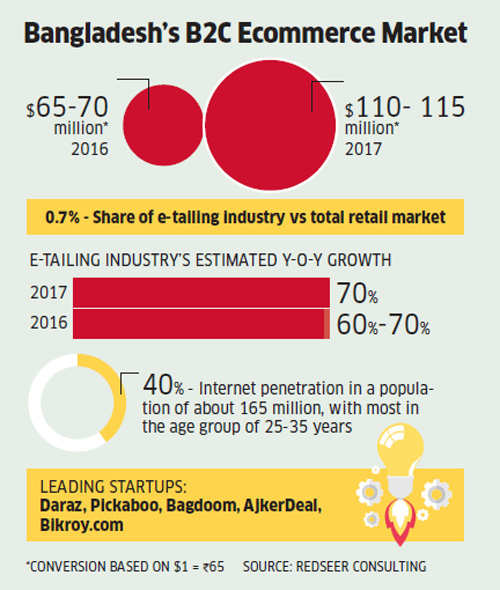
The rollout of 3G internet in Bangladesh 3-4 years ago led to rapid adoption of online shopping there. The country’s e-tailing sector is expected to grow 70% in 2017, according to RedSeer Consulting. Internet penetration to 40% of Bangladesh’s 165-million population has bolstered the growth of local ecommerce, F-commerce (merchants conducting online business through Facebook pages) and e-grocery startups.
Rocket Internet-backed online marketplace Daraz, Foxconn-backed e-retailer Pickaboo, and Chaldal are among the leading startups in this fairy nascent ecosystem. The size of Bangladesh’s ecommerce market is estimated to be $110-115 million this year, which is a mere 0.7% of the country’s total retail market, according to RedSeer Consulting. To put that in perspective, India’s ecommerce market is estimated to cross $17 billion this year.
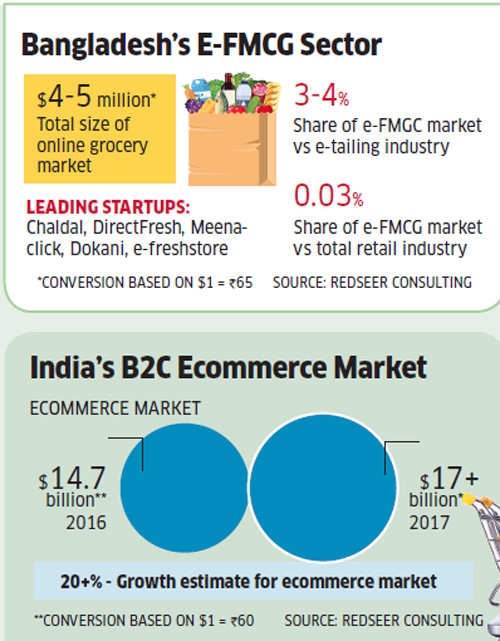

Rocket Internet-backed online marketplace Daraz, Foxconn-backed e-retailer Pickaboo, and Chaldal are among the leading startups in this fairy nascent ecosystem. The size of Bangladesh’s ecommerce market is estimated to be $110-115 million this year, which is a mere 0.7% of the country’s total retail market, according to RedSeer Consulting. To put that in perspective, India’s ecommerce market is estimated to cross $17 billion this year.
The size of Bangladesh’s egrocery market is much smaller at $4-5 million, or about 0.03% of the country’s overall grocery market. Even so, analysts are predicting that Bangladesh’s ecommerce market will surge to $20 billion by 2020, by when, according to Goldman Sachs, India’s online retail market is expected to reach $69 billion.



Bangladesh’s ecommerce market is “nascent but growing— similar to what India was probably seven years ago. It’s a good time for ecommerce players to be entering,” said Shalini Prakash, venture partner at 500 Startups, which has invested in more than 50 companies in India since 2011.
“We are a global fund. So we are looking at founders and startups that are looking to solve interesting problems across the globe for the local market.”
Daraz, founded in 2014, dominates Bangladesh’s ecommerce market, selling electronics, mobile phones, large appliances and apparel. The company is growing at double-digit percentages every month, supplying to customers in neighbouring markets Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Nepal and Myanmar as well.
The opportunity in Bangladesh prompted Delhi-based digital marketing company MoMagic Technologies to launch Pickaboo there last year. “The Bangladesh ecommerce market is close to five years behind the Indian ecommerce market and is around 10-12% of the size of the Indian ecommerce market,” said Arun Gupta, chief executive of MoMagic. “We identified Bangladesh as a potential opportunity and decided to launch Pickaboo.”
“We are a global fund. So we are looking at founders and startups that are looking to solve interesting problems across the globe for the local market.”
Daraz, founded in 2014, dominates Bangladesh’s ecommerce market, selling electronics, mobile phones, large appliances and apparel. The company is growing at double-digit percentages every month, supplying to customers in neighbouring markets Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Nepal and Myanmar as well.
The opportunity in Bangladesh prompted Delhi-based digital marketing company MoMagic Technologies to launch Pickaboo there last year. “The Bangladesh ecommerce market is close to five years behind the Indian ecommerce market and is around 10-12% of the size of the Indian ecommerce market,” said Arun Gupta, chief executive of MoMagic. “We identified Bangladesh as a potential opportunity and decided to launch Pickaboo.”
Pickaboo, which clocks monthly revenues of $600,000, mostly sells electronics on its controlled marketplace and has plans to add leather accessories shortly.
“When Flipkart was launched, they started selling books first— a category where what you see on the marketplace and what you receive is the same. In today’s world, electronics fall under this category with the probability of difference being low,” said Gupta, adding that Pickaboo has a 20% share of Bangladesh’s ecommerce market.
“When Flipkart was launched, they started selling books first— a category where what you see on the marketplace and what you receive is the same. In today’s world, electronics fall under this category with the probability of difference being low,” said Gupta, adding that Pickaboo has a 20% share of Bangladesh’s ecommerce market.
International Finance Corporation (IFC), the private sector lending and investment arm of the World Bank, has been tracking Bangladesh’s entrepreneurial ecosystem the past year and is bullish about the market.
It has shortlisted and is actively monitoring 43 startups, including Chaldal topping the list as a potential investee company.
It has shortlisted and is actively monitoring 43 startups, including Chaldal topping the list as a potential investee company.
Chaldal, somewhat similar to India’s largest e-grocer Big Basket, delivers groceries using a network of small warehouses spread across Dhaka. “We launched Chaldal because we felt that there was a need to offer more variety of groceries to our customers,” said CEO Alim. “As the country develops there is a need to provide services that save time for the growing middle class.”
Chaldal competes with Direct Fresh and Meena Click, the online extension of Bangladesh’s 15-year-old supermarket chain Meena Bazaar. Specialising in groceries and personal care products, Meena Click was launched three years ago. The company, which handles 4,000-4,500 orders a month in Dhaka and the port city of Chittagong, said it has doubled its business over the past year.
Chaldal competes with Direct Fresh and Meena Click, the online extension of Bangladesh’s 15-year-old supermarket chain Meena Bazaar. Specialising in groceries and personal care products, Meena Click was launched three years ago. The company, which handles 4,000-4,500 orders a month in Dhaka and the port city of Chittagong, said it has doubled its business over the past year.
“The grocery market is huge with limited superstore penetration and we feel that the online model would help us achieve scale that no other player in the market has,” said Alim. The online grocery startup reached out to its counterparts across the world, including Indian companies Big Basket and Grofers, to exchange notes. “The learning has mostly been around what (Big Basket and Grofers) think is important to customers— tradeoffs between quality, speed, etc.,” said Alim.
This also led to a realization that despite the geographical proximity, Bangladeshi startups operated in a different environment.
“Indian players have been able to use capital to get a starting boost. Grofers, for example, for fast-growth by spending on marketing, while Big Basket invested heavily in operations and getting quality right,” said Alim.
Due to Bangladesh’s rapidly growing economy and urban population, IFC believes now is the right time to make some early bets in the country’s startup ecosystem. “The metrics point to healthy growth in Bangladesh… We are looking at some earlierstage investments than what we do in India—most likely at the series-A level financing along with other investors,” said Shukla.
This also led to a realization that despite the geographical proximity, Bangladeshi startups operated in a different environment.
“Indian players have been able to use capital to get a starting boost. Grofers, for example, for fast-growth by spending on marketing, while Big Basket invested heavily in operations and getting quality right,” said Alim.
Another aspect about this nascent ecommerce market is that of the total online spending by customers, which is estimated to be about $50 million, 40% of the transactions are through 15,000 small merchants selling through their Facebook pages.
Bangladesh’s ecommerce “ecosystem, instead of developing around one or two big players, has several smaller merchants who sell online,” said Ruchira Shukla, regional lead, South Asia, venture capital, at IFC, which is also an investor in India’s biggest online grocer Big Basket.
Bangladesh’s ecommerce “ecosystem, instead of developing around one or two big players, has several smaller merchants who sell online,” said Ruchira Shukla, regional lead, South Asia, venture capital, at IFC, which is also an investor in India’s biggest online grocer Big Basket.
Due to Bangladesh’s rapidly growing economy and urban population, IFC believes now is the right time to make some early bets in the country’s startup ecosystem. “The metrics point to healthy growth in Bangladesh… We are looking at some earlierstage investments than what we do in India—most likely at the series-A level financing along with other investors,” said Shukla.
Bangladesh also has the advantage of a large and homogenous population of 165 million. Because of this, “once the business model is figured out, it can be scaled across several cities and the entrepreneur doesn’t have to worry about differences in language or culture,” Shukla said.
That said, Bangladesh has fewer large and dense cities when compared with India, which poses tough limitations to growth by expansion.
That said, Bangladesh has fewer large and dense cities when compared with India, which poses tough limitations to growth by expansion.
The market is fraught with several other challenges too. “Logistics and the transportation system are still challenges in Bangladesh,” said a spokesperson for Daraz, which said it has the largest delivery network in the country, with its own fleet operating in 20 cities. “Also, the stagnant traffic hampers fast delivery of products.”
Educating customers is also an uphill task. Alim recalled being at the receiving end of “a lot of snarky remarks related to a Wharton education going to waste on becoming a grocer. People still think that I might end up doing something ‘real’ later in life.” Consumer brands, too, used to be skeptics. “When we started Chaldal, we could not find good pictures of the products we were selling (for a catalogue) and companies like Unilever were not helpful in providing us with pack shots,” said Alim.
Then, he had his light-bulb moment.
The Chaldal team rented out a small grocery for two hours to click pictures of all the items it stocked to build their online catalogue.
“Basically, we paid some money to keep the store open for an extra two hours and set up a photo studio inside. The pictures looked horrible but at least we got them up on a website.”
The Chaldal team rented out a small grocery for two hours to click pictures of all the items it stocked to build their online catalogue.
“Basically, we paid some money to keep the store open for an extra two hours and set up a photo studio inside. The pictures looked horrible but at least we got them up on a website.”
Another big challenge lies in how to turn around the market despite a shortage of capital. This has forced some companies to resort to capital-efficiency to survive.
“Part of the capital-efficiency comes from us having very little capital available in the ecosystem— we have had to innovate significantly beyond the practices in the Indian market,” said Alim, who took inspiration from Big Basket’s warehouse to start their own in Dhaka. Chaldal now has five small warehouses and one sourcing hub in Dhaka.
“Part of the capital-efficiency comes from us having very little capital available in the ecosystem— we have had to innovate significantly beyond the practices in the Indian market,” said Alim, who took inspiration from Big Basket’s warehouse to start their own in Dhaka. Chaldal now has five small warehouses and one sourcing hub in Dhaka.
No comments:
Post a Comment